# Load packages
library(wbstats)
library(dplyr)
library(janitor)
# Store the list of indicators in an object
indicators <- c("flfp" = "SL.TLF.CACT.FE.ZS", "women_rep" = "SG.GEN.PARL.ZS")
# Download the data
wb_dta <- wb_data(indicators, mrv = 25) |> # most recent 25 years
select(!iso2c) |>
rename(year = date) |>
mutate(
flfp = round_to_fraction(flfp, denominator = 100), # round to nearest 100th
women_rep = round_to_fraction(women_rep, denominator = 100)
)
# View the data
glimpse(women_emp) Merging Data Frames
June 22, 2025
What is a Join
Horizontal Join (Merge)
- Often we have data from two different sources
- Results in two data frames
- How to make them one so we can analyze?
Illustration
Source: R for HR
Types of Joins in dplyr
- Mutating versus filtering joins
- Four types of mutating joins
inner_join()full_join()left_join()right_join()
- For the most part we will use
left_join()
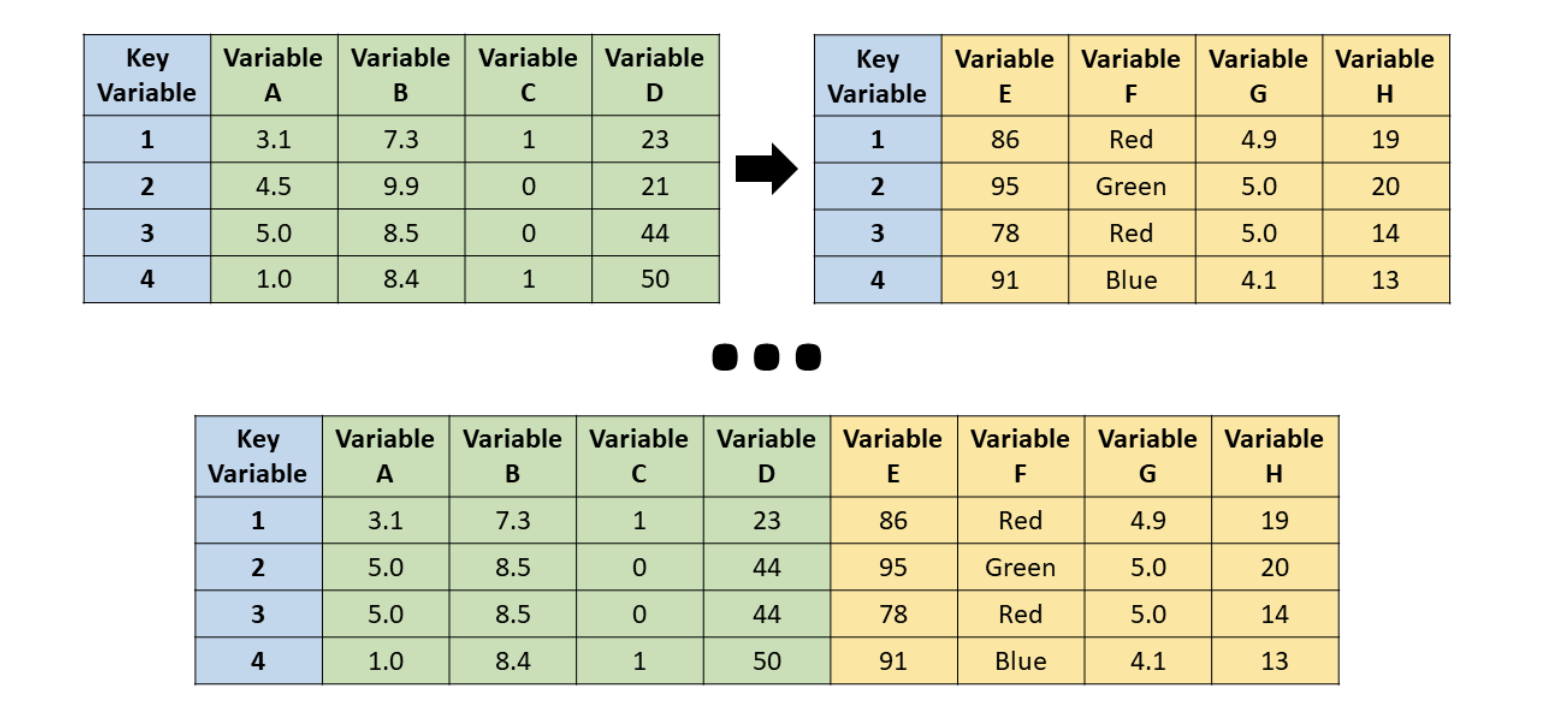
inner_join()
Source: R for HR
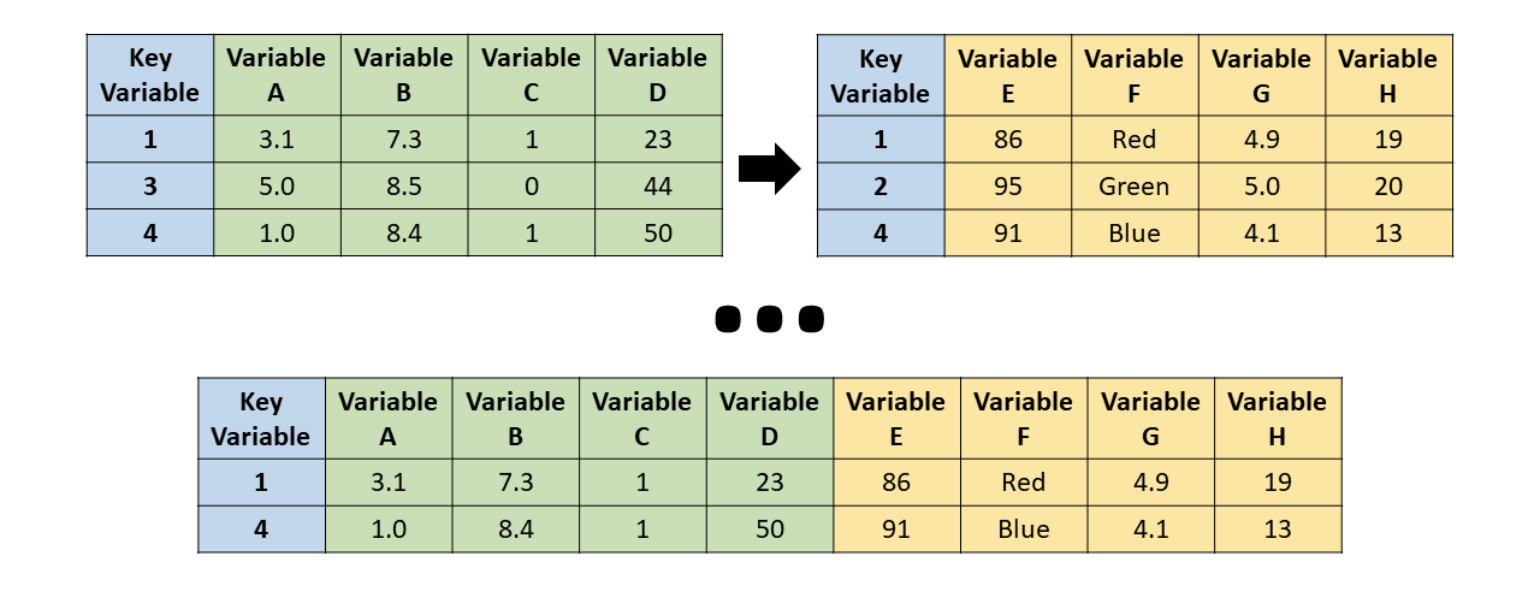
full_join()
Source: R for HR
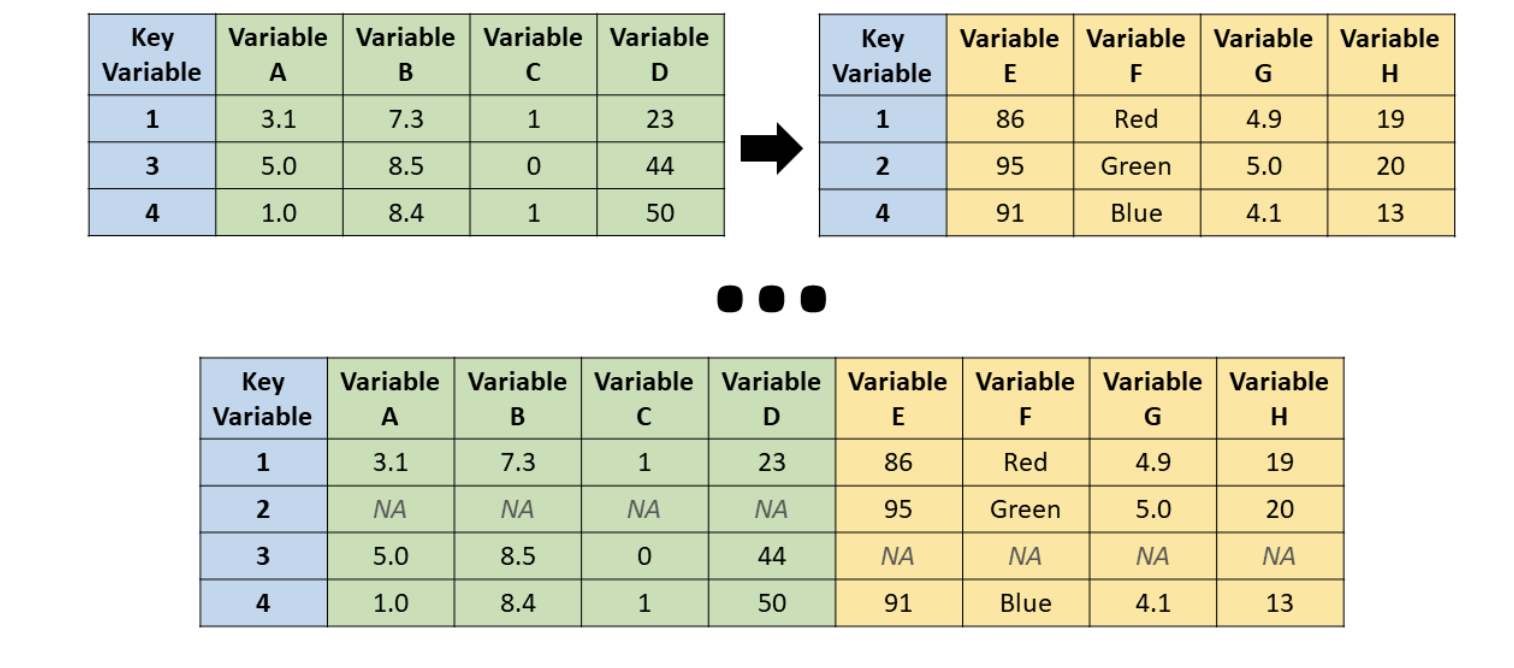
left_join()
Source: R for HR
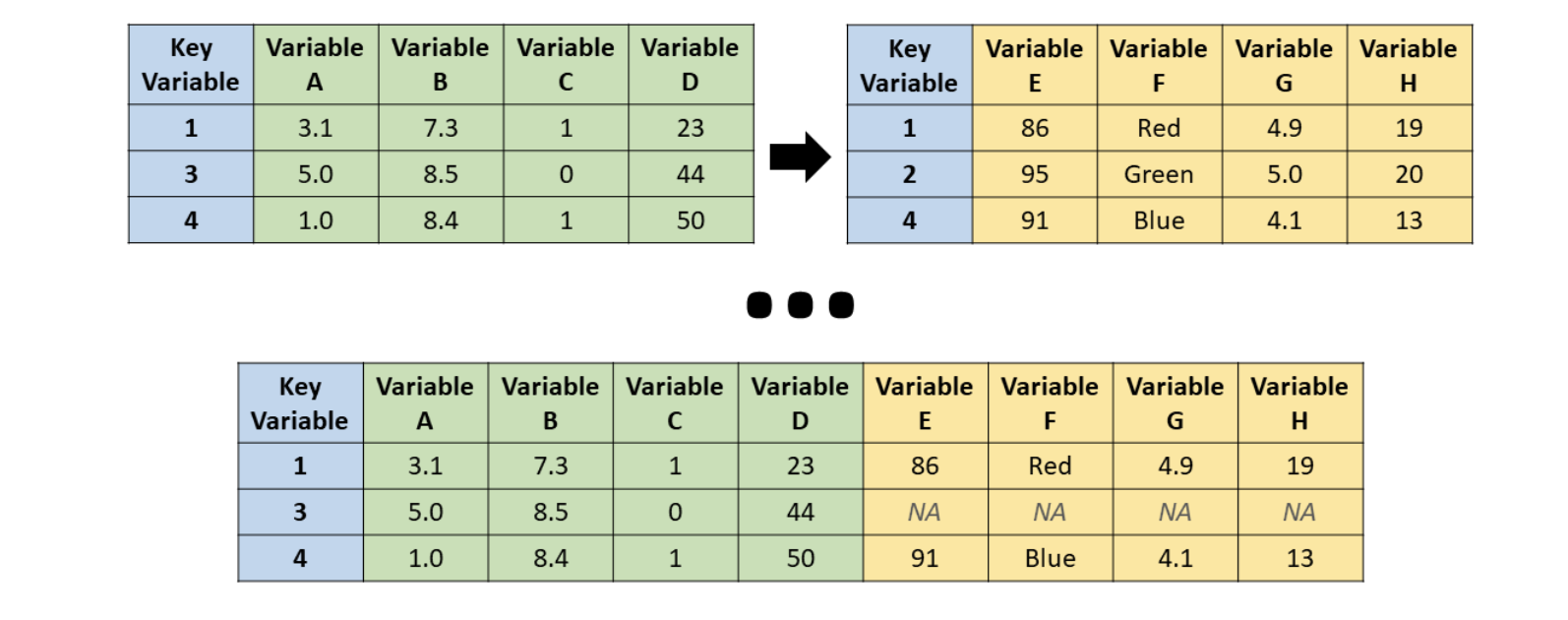
right_join()
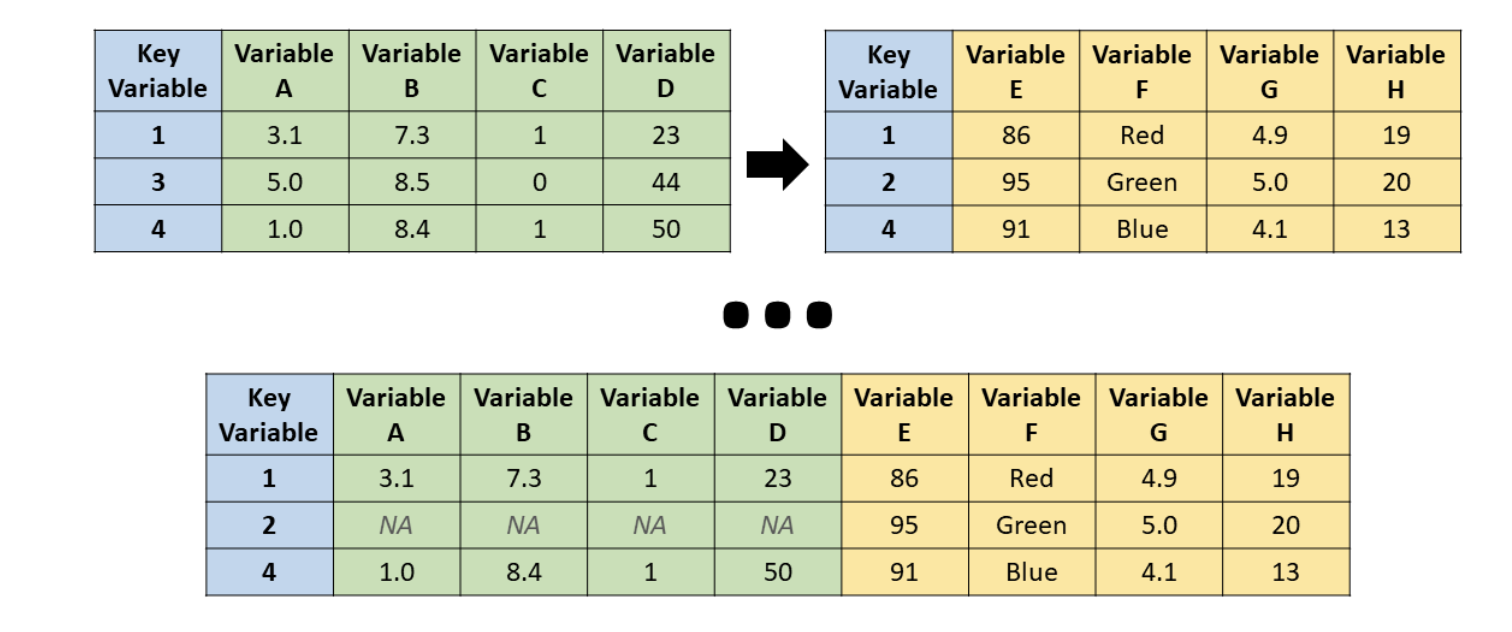
Source: R for HR
Worked Example
Scenario
- We want to merge two data frames
- One is from the World Bank
- The other is from V-Dem
- How do we do it?
Grab Some WB Data
Grab Some V-Dem Data
library(vdemlite)
vdem_dta <- fetchdem(indicators = c("v2x_gender", "v2x_gencl", "e_regionpol_6C") |>
start_year = 2000, end_year = 2020) |> # 20 year span
rename(
women_polemp = v2x_gender,
women_civlib = v2x_gencl,
region = e_regionpol_6C
) |>
mutate(
region = case_match(region,
1 ~ "Eastern Europe",
2 ~ "Latin America",
3 ~ "Middle East",
4 ~ "Africa",
5 ~ "The West",
6 ~ "Asia")
)
glimpse(vdem_dta)Key Questions
- What is the unit of analysis?
- What is/are the corresponding identifier variables?
- Are the identifier variables in common?
- Or do they have to be added/transformed to match?
Merging WB and V-Dem Data
- These are both time-series, country-level data
- Need to merge by country-year
- Year is easy
- But there are many different country codes
- Can use
countrycodepackage to assign country codes
Use countrycode
# Load countrycode
library(countrycode)
# Create new iso3c variable
vdem_data <- vdem_data |>
mutate(iso3c = countrycode(sourcevar = country_id, # what we are converting
origin = "vdem", # we are converting from vdem
destination = "wb")) |> # and converting to the WB iso3c code
relocate(iso3c, .after = country_id) # move iso3c
# View the data
glimpse(dem_data)Try it Yourself
- Using your democracy data frame from the last lesson
- Use
mutate()andcountrycode()to add iso3c country codes - Use
relocateto move your iso3c code to the “front” of your data frame (optional)
10:00
Use left_join() to Merge
Try it Yourself
- Take your V-Dem data frame and your World Bank data frame
- Using
left_join()to merge on country code and year - Along the way, use
rename()andselect()to insure you have just one country name - Try
inner_join(),full_join(), andright_join()as time allows
10:00
Summarize the Data
- Do a group, summarize, arrange sequence on your merged data frame
- Group and summarize by country (mean or median)
- Try using
across()to summarize multiple columns at once
10:00
Create a Scatter Plot
- Now you have one data point per country
- Use
ggplot2to create a scatter plot
10:00
